

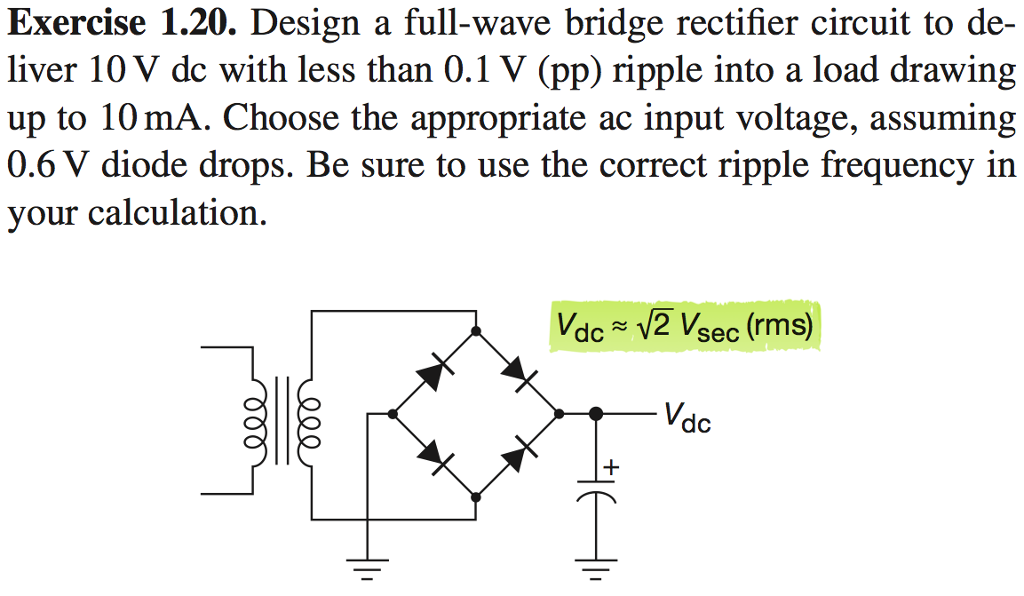
In real-life application, the load is 5 series-connect 100W LED. The transformer is PCB mounted and it is a 1-ampere 13-volt transformer. Simple project to deliver high-voltage at high-current to a DC load, controlled with PWM. Just the opposite is called a step-down transformer.Ī step-down transformer is used to convert the high voltage AC to the low voltage AC. Primary winding turns) is called a step– up transformer Step Down Transformer They form a bridge converter which is a building block for the converter and after converting there is a capacitor. These four diodes are used to convert the 13V AC output across the transformer. Four rectifier diode 1N4007 is used to rectify the AC input. There are 2 basic types of transformers: Step Up Transformerįrom primary(input) to secondary(output) (more secondary winding turns than The transformer is used to step down the 230V AC to 13V AC. The LDO, IC1 is also connected to regulate the output voltage. They form a bridge converter which is a building block for the converter and after converting there is a capacitor installed to smooth the AC output signal & that capacitor is called FILTER CAPACITOR C1. The formula is very useful if you understand what it means.The transformer is used to step down the 230V AC to 13V AC. Some loads require high currents, others high volta ges, and others both high current and high voltage. A more common arrangement is to allow the rectifier to work into a large smoothing capacitor which acts as a reservoir. The ripple voltage is very large in this situation the peak-to-peak ripple voltage is equal to the peak AC voltage. Specify the voltage ratings of your components, such as the filterĬapacitor. Because a bridge rectifier produces a full-wave output, the formula for calculating average DC value is the same as that given for the full-wave rectifier: This equation tells us that the DC value of a full-wave signal is about 63.6 percent of the peak value. Visintini Elettra Synchrotron Light Laboratory, Trieste, Italy Abstract In particle accelerators, rectifiers are u sed to convert the AC voltage into DC or low-frequency AC to supply loads like magnets or klystrons. The simplest scenario in AC to DC conversion is a rectifier without any smoothing circuitry at all.
#AC TO DC BRIDGE RECTIFIER CALCULATOR PLUS#
That value is very important when it is time to This example shows an ideal AC transformer plus full-wave bridge rectifier. Theįormula tells you the maximum dc voltage you can achieve from a given You are missing the point of the formula if you think it is wrong. The RMS-to-Peak formula is correct but only under ideal conditions, and as you might have guessed by now, real-world conditions dominate once you apply a load or use a inverter/UPS for AC power, making the RMS to Peak formula useless, especially under heavy made an important observation
#AC TO DC BRIDGE RECTIFIER CALCULATOR FULL#
The output voltage will drop as the load increases until a full safe load is reached.īy now the peaking effect is gone and the DC voltage is more like the AC-RMS value. At high current levels >10 amps the Vdrop across each diode can be 1 volt. With heavier loads a bridge or full-wave rectifier will provide the most current. 7 volts or 1.4 volts from the expected peak, and the numbers should match better. 1% of capacity will drop the voltage by the amount the diodes dropped. This peak voltage assumes no load, whether a single diode is used or a bridge rectifier, plus capacitor of sufficient value to remove any AC ripple. Some UPS's and DC-AC inverters put out a choppy sine wave that would make the 1.414 ratio of RMS value to peak value not true. The sites formula is correct, but only under ideal conditions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
